-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Ancient Civilizations
Invention of Writing
3500 BCE
% complete
The invention of writing, which occurred around 3500 BCE, marked a significant turning point in human history. It allowed for the recording and preservation of knowledge, paving the way for the development of complex societies and the transmission of ideas across generations.
Image source: Writing

Construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza
2560 BCE
% complete
The construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza, completed around 2560 BCE, stands as a testament to the engineering prowess of the ancient Egyptians. This architectural marvel served as a burial site for the pharaoh Khufu and remains one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Image source: Great Pyramid of Giza

Fall of the Roman Empire
476 CE
% complete
The fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE marked the end of classical antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of this once-mighty empire had far-reaching consequences, leading to political fragmentation, cultural shifts, and the rise of new powers in Europe.
Image source: Fall of the Western Roman Empire
Middle Ages and Renaissance
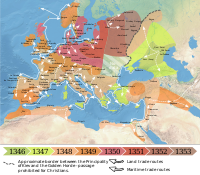
The Black Death
1347 CE - 1351 CE
% complete
The Black Death, a devastating pandemic caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, swept through Europe in the mid-14th century. This plague, with its high mortality rates, had profound social, economic, and cultural impacts, reshaping the fabric of medieval society and paving the way for significant changes in the ensuing Renaissance period.
Image source: Black Death
Scientific Revolution
1500 - 1699
% complete
The Scientific Revolution, which unfolded in the 16th and 17th centuries, marked a paradigm shift in the way humans understood the natural world. Pioneered by figures like Nicolaus Copernicus, Galileo Galilei, and Isaac Newton, this intellectual movement laid the foundations for modern science and challenged long-held beliefs.
Image source: Scientific Revolution

Age of Exploration and Colonization
Age of Exploration
1400 - 1699
% complete
The Age of Exploration, spanning the 15th to the 17th centuries, saw European explorers embark on ambitious voyages of discovery. Led by figures such as Christopher Columbus, Vasco da Gama, and Ferdinand Magellan, these expeditions opened up new trade routes, expanded European influence, and forever altered the global map.
Image source: Age of Discovery

Modern Era and Globalization
Industrial Revolution
1700 - 1899
% complete
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, marked a transformative shift in manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture. It introduced mechanization, steam power, and factory production, leading to significant economic and social changes that fueled the rise of modern industrial societies.
Image source: Industrial Revolution

American Revolution
1775 - 1783
% complete
The American Revolution, fought from 1775 to 1783, resulted in the independence of the thirteen American colonies from British rule. This historic event established the United States as a new nation and inspired subsequent struggles for independence around the world.
Image source: American Revolution

French Revolution
1789 - 1799
% complete
The French Revolution, spanning from 1789 to 1799, was a period of radical political and social upheaval in France. It led to the overthrow of the monarchy, the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte, and the spread of revolutionary ideals that would shape the course of European history.
Image source: French Revolution

World War I
1914 - 1918
% complete
World War I, fought from 1914 to 1918, was a global conflict that involved major powers from around the world. The war's unprecedented scale, technological advancements, and devastating human toll reshaped the geopolitical landscape and laid the groundwork for subsequent conflicts.
Image source: World War I

Russian Revolution
1917
% complete
The Russian Revolution of 1917 marked the overthrow of the Russian monarchy and the establishment of a socialist government. Led by Vladimir Lenin and the Bolshevik Party, this revolution had profound consequences, including the formation of the Soviet Union and the spread of communist ideologies.
Image source: Russian Revolution

World War II
1939 - 1945
% complete
World War II, spanning from 1939 to 1945, was a global conflict involving many nations and resulting in immense human suffering and loss of life. The war witnessed the rise of totalitarian regimes, the Holocaust, and the use of atomic weapons, ultimately leading to the reshaping of the world order.
Image source: World War II

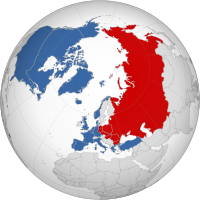
Cold War
1947 - 1991
% complete
The Cold War, a prolonged period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, lasted from 1947 to 1991. Characterized by ideological rivalry, proxy wars, and the threat of nuclear annihilation, this standoff shaped global politics and had a profound impact on international relations.
Image source: Cold War
Space Race
1955 - 1972
% complete
The Space Race, which unfolded between the United States and the Soviet Union from 1955 to 1972, was a competition to achieve milestones in space exploration. This rivalry led to groundbreaking achievements such as the first human in space (Yuri Gagarin) and the moon landing (Apollo 11), pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and technological capabilities.
Image source: Space Race

Fall of the Berlin Wall
Nov 9, 1989
% complete
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the end of the Cold War and the reunification of East and West Germany. This event marked a turning point in European history and the dismantling of the Iron Curtain, paving the way for a new era of geopolitical realignment.
Image source: Fall of the Berlin Wall

End of Apartheid
Apr 27, 1994
% complete
The end of apartheid in South Africa, marked by the first universal elections held on April 27, 1994, was a significant milestone in the country's history. This peaceful transition to democracy, led by Nelson Mandela, brought an end to institutionalized racial segregation and set the stage for reconciliation and nation-building.
Image source: Negotiations to end apartheid in South Africa

September 11 Attacks
Sep 11, 2001
% complete
The September 11 attacks, carried out by the terrorist group Al-Qaeda in 2001, were a series of coordinated attacks on the United States. These tragic events resulted in the loss of thousands of lives and had far-reaching consequences, including the launch of the War on Terror and a reevaluation of global security measures.
Image source: September 11 attacks

Arab Spring
2010 - 2012
% complete
The Arab Spring, a series of pro-democracy uprisings that began in 2010, swept across several countries in the Middle East and North Africa. These mass protests and revolutions aimed to challenge authoritarian regimes, demand political reforms, and promote social justice, leading to significant political and social transformations in the region.
Image source: Arab Spring

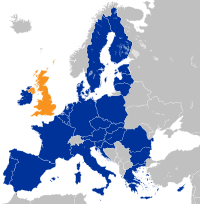
Brexit
Jun 23, 2016
% complete
Brexit refers to the withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union, following a referendum held on June 23, 2016. This decision had profound implications for the UK's political, economic, and social landscape and signaled a shift in the European integration project.
Image source: Brexit
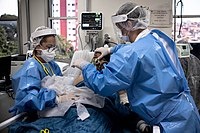
COVID-19 Pandemic
Dec 2019 - Present
% complete
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, emerged in late 2019 and continues to impact the world. This global health crisis has led to widespread illness, loss of life, economic disruptions, and significant changes in daily life, highlighting the interconnectedness of our modern world.
Image source: COVID-19 pandemic
Key Facts
- 3000 BC: The ancient civilization of Egypt emerges along the Nile River.
- 476 AD: The fall of the Western Roman Empire marks the end of ancient Rome.
- 1492: Christopher Columbus explores the Americas, leading to European colonization.
- 1945: World War II ends with the defeat of Nazi Germany and Japan.
- 2001: The September 11 attacks in the United States have a major impact on world politics and security.
Source
This World history timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].