-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Cell Theory Timeline
(1665 - Present)Cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that states all living organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms, and new cells can only arise from pre-existing cells. This timeline explores the development of cell theory from the discovery of the microscope to the modern cell theory. More Less
Early Observations
Robert Hooke's Observations
1665
% complete
Robert Hooke, an English scientist, publishes "Micrographia," describing his observations of cells in cork, marking one of the earliest recorded observations of cells.
Image source: Robert Hooke

Antonie van Leeuwenhoek's Microscopy Discoveries
1674
% complete
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch scientist, observes and describes living microorganisms through his improved microscope, providing further evidence of the existence of cells.
Image source: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek

Cell Theory Formulation
Matthias Schleiden's Plant Cell Observations
1838
% complete
Matthias Schleiden, a German botanist, proposes that plants are composed of cells after observing plant tissues and recognizing their structural similarities.
Image source: Matthias Jakob Schleiden

Theodor Schwann's Animal Cell Observations
1839
% complete
Theodor Schwann, a German physiologist, concludes that animal tissues are also composed of cells, expanding upon Schleiden's findings and contributing to the formulation of the cell theory.
Image source: Theodor Schwann

Rudolf Virchow's Cellular Pathology
1855
% complete
Rudolf Virchow, a German physician, introduces the concept of cellular pathology, stating that all cells arise from pre-existing cells, emphasizing the importance of cell division in growth and disease.
Image source: Rudolf Virchow

Louis Pasteur's Germ Theory
1861
% complete
Louis Pasteur's experiments and observations support the germ theory, which further reinforces the concept of cells as the fundamental units of life.
Image source: Louis Pasteur

Microscopy Advancements
Development of Electron Microscopy
1931
% complete
Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll develop the first electron microscope, allowing for higher magnification and resolution in cell imaging.
Image source: Electron microscope

Development of Confocal Microscopy
1957
% complete
Marvin Minsky develops confocal microscopy, enabling the visualization of cells and tissues in unprecedented detail and clarity.
Image source: Confocal microscopy

Modern Cell Research
James Watson and Francis Crick's DNA Structure
1953
% complete
James Watson and Francis Crick propose the double-helix structure of DNA, unraveling the genetic code and revolutionizing our understanding of cellular inheritance.
Image source: James Watson

Discovery of Ribosomes
1955
% complete
George Palade identifies and characterizes ribosomes, cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis, providing insights into the cellular machinery.
Image source: Ribosome
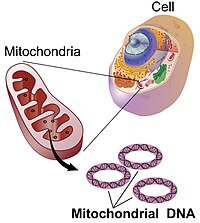
Discovery of Mitochondrial DNA
1963
% complete
Margit and Sylvan Nass identify mitochondrial DNA, a separate genetic material within mitochondria, contributing to our understanding of cellular energy production and evolution.
Image source: Mitochondrial DNA
Discovery of Stem Cells
1963
% complete
Ernest McCulloch and James Till discover stem cells, demonstrating their ability to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types, opening up new avenues for regenerative medicine and understanding development.
Image source: Stem cell
Organoid Cultures
2009
% complete
Hans Clevers and colleagues develop organoid cultures, enabling the growth of miniature organs in the lab, providing valuable models for studying human development, diseases, and drug testing.
Image source: Organoid

Development of CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing
2012
% complete
Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier develop the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing tool, revolutionizing genetic engineering and offering precise control over cellular DNA.
Image source: CRISPR

Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
2013
% complete
Aviv Regev and colleagues pioneer single-cell RNA sequencing techniques, allowing for the analysis of gene expression in individual cells, leading to a deeper understanding of cellular heterogeneity.
Image source: Single-cell sequencing

Key Facts
- 1665: Robert Hooke discovers cells in cork under a microscope.
- 1674: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek observes single-celled organisms under a microscope.
- 1838-1839: Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann propose the cell theory.
- 1858: Rudolf Virchow adds the concept of cell division to the cell theory.
- Modern cell theory includes the idea that cells contain DNA and have the ability to differentiate.
Source
This Cell Theory timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].