-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Foundational Discoveries
Wilhelm Wundt establishes the first psychology laboratory
1879
% complete
Wilhelm Wundt, often regarded as the father of experimental psychology, establishes the first psychology laboratory at the University of Leipzig, Germany. This marks the beginning of psychology as a scientific discipline.
Image source: Wilhelm Wundt

Edward Thorndike's law of effect
1898
% complete
Edward Thorndike formulates the law of effect, stating that behaviors followed by positive consequences are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by negative consequences are less likely to be repeated.
Image source: Edward Thorndike

Sigmund Freud introduces psychoanalysis
1899
% complete
Sigmund Freud publishes "The Interpretation of Dreams," introducing psychoanalysis as a method for understanding the unconscious mind and revolutionizing the field of psychology.
Image source: Sigmund Freud

Ivan Pavlov's experiments on classical conditioning
1903
% complete
Ivan Pavlov's experiments with dogs demonstrate classical conditioning, showing how behaviors can be learned through associations between stimuli and responses.
Image source: Ivan Pavlov

John B. Watson's "Little Albert" experiment
1920
% complete
John B. Watson conducts the "Little Albert" experiment, demonstrating the principles of classical conditioning by conditioning a fear response in a young child.
Image source: John B. Watson

B.F. Skinner's operant conditioning experiments
1938
% complete
B.F. Skinner conducts experiments on operant conditioning, demonstrating how behavior can be shaped through reinforcement or punishment.
Image source: B. F. Skinner

Stanley Schachter's two-factor theory of emotion
1962
% complete
Stanley Schachter proposes the two-factor theory of emotion, suggesting that emotions are the result of physiological arousal combined with cognitive interpretation.
Image source: Stanley Schachter

Prominent Figures
Carl Rogers introduces client-centered therapy
1942
% complete
Carl Rogers develops client-centered therapy, emphasizing the importance of empathy, unconditional positive regard, and active listening in therapeutic relationships.
Image source: Carl Rogers

Harry Harlow's experiments on attachment in monkeys
1958
% complete
Harry Harlow conducts experiments on infant rhesus monkeys, demonstrating the importance of social and emotional bonds in early development.
Image source: Harry Harlow

Stanley Milgram's obedience experiments
1961
% complete
Stanley Milgram conducts a series of controversial experiments on obedience, revealing the willingness of individuals to obey authority figures, even when it conflicts with their personal conscience.
Image source: Milgram experiment
Albert Bandura's Bobo doll experiment
1961
% complete
Albert Bandura conducts the Bobo doll experiment, demonstrating the power of observational learning and the influence of role models on behavior.
Image source: Albert Bandura

Roger Sperry's split-brain research
1961
% complete
Roger Sperry's split-brain research, conducted on patients with severed corpus callosums, reveals the specialization of brain hemispheres and their distinct functions.
Image source: Roger Wolcott Sperry

Mary Ainsworth's Strange Situation experiment
1970
% complete
Mary Ainsworth develops the Strange Situation experiment to study attachment patterns in infants, leading to the identification of different attachment styles.
Philip Zimbardo's Stanford Prison Experiment
1971
% complete
Philip Zimbardo conducts the Stanford Prison Experiment, revealing the powerful impact of situational factors on human behavior and the potential for abuse of power.
Image source: Stanford prison experiment

Elizabeth Loftus' research on false memories
1974
% complete
Elizabeth Loftus conducts groundbreaking research on the malleability of human memory, demonstrating how false memories can be implanted and how eyewitness testimony can be influenced.
Image source: Elizabeth Loftus

Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky's research on cognitive biases
1974
% complete
Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky collaborate on research that uncovers numerous cognitive biases, challenging the assumption of human rationality in decision-making.
Image source: Daniel Kahneman

Psychological Disorders and Treatments
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) first published
1952
% complete
The American Psychiatric Association publishes the first edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), providing a standardized classification system for mental disorders.
Image source: DSM-5

Albert Ellis develops Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT)
1955
% complete
Albert Ellis develops Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), a form of cognitive-behavioral therapy that emphasizes challenging irrational beliefs to promote emotional well-being.
Aaron Beck develops cognitive therapy
1960
% complete
Aaron Beck develops cognitive therapy, a form of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns to treat mental health conditions.
Image source: Aaron Beck

Research Methods and Techniques
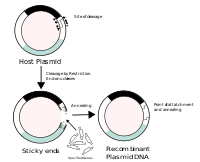
Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer create the first recombinant DNA molecule
1973
% complete
Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer successfully create the first recombinant DNA molecule, a significant breakthrough in genetic engineering and biotechnology.
Image source: Recombinant DNA
Key Facts
- 1879: Wilhelm Wundt establishes the first psychology research laboratory in Leipzig, Germany.
- 1900: Sigmund Freud publishes 'The Interpretation of Dreams,' introducing psychoanalysis.
- 1913: John B. Watson publishes 'Psychology as the Behaviorist Views It,' marking the beginnings of behaviorism.
- 1957: Abraham Maslow introduces the concept of self-actualization and the hierarchy of needs in his publication 'Motivation and Personality.'
- 1967: Martin Seligman pioneers the field of positive psychology, focusing on human strengths and positive emotions.
Source
This History of Psychology timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].