-
Use Cases
-
Resources
-
Pricing
Greek Golden Age Timeline
(5th century BC)The Greek Golden Age was a period of major cultural and intellectual advancements in ancient Greece.
Architecture and Engineering
Construction of the Temple of Hera at Olympia begins
590 BC
% complete
Construction of the Temple of Hera at Olympia begins (590 BC).
Image source: Ancient Greek architecture

Construction of the Temple of Artemis at Corfu
580 BC
% complete
Construction of the Temple of Artemis at Corfu (580 BC) - The Temple of Artemis was constructed on the Greek island of Corfu during the 6th century BC. It was dedicated to Artemis, the goddess of hunting and the moon. The temple was built in the Doric style and featured intricate architectural details. It served as a place of worship and a testament to the wealth and power of Corfu during the Greek Golden Age.
Construction of the Temple of Apollo at Syracuse begins
570 BC
% complete
Construction of the Temple of Apollo at Syracuse begins (570 BC).
Construction of the Temple of Apollo at Delphi begins
548 BC
% complete
Construction of the Temple of Apollo at Delphi begins (548 BC)
Image source: Temple of Apollo (Delphi)

Construction of the Temple of Apollo Epicurius at Bassae begins
450 BC - 400 BC
% complete
Construction of the Temple of Apollo Epicurius at Bassae begins (450 BC - 400 BC)
Construction of the Temple of Hephaestus in Athens
449 BC - 415 BC
% complete
Construction of the Temple of Hephaestus in Athens took place between 449 BC and 415 BC. The temple, dedicated to the Greek god Hephaestus, was designed by the architect Ictinus and built under the supervision of the sculptor Phidias. It is the best-preserved ancient Greek temple that still stands today, and is considered a masterpiece of Classical architecture. The construction of the temple was part of a larger building program on the Athenian Acropolis, which also included the construction of the Parthenon.
Image source: Temple of Hephaestus

Construction of the Parthenon begins
447 BC - 432 BC
% complete
Construction of the Parthenon begins (447 BC - 432 BC). The Parthenon is a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena and is located on the Acropolis of Athens, Greece. It was built during the height of the Athenian Empire and is considered one of the greatest examples of ancient Greek architecture. The construction of the Parthenon began in 447 BC under the supervision of the sculptor Phidias and the architects Ictinus and Callicrates. It took approximately 15 years to complete, with the building being officially completed in 432 BC.
Image source: Parthenon Frieze

Construction of the Temple of Poseidon at Cape Sounion
444 BC
% complete
Construction of the Temple of Poseidon at Cape Sounion is completed. The temple is located on a promontory at the southernmost tip of Attica, near Athens, Greece. It is dedicated to the Greek god Poseidon, god of the sea. The temple is built between 444 and 440 BC, during the Greek Golden Age. The architect of the temple is unknown, but it is believed to be designed by the same architect who built the Parthenon in Athens. The temple is made of marble and features Doric columns. It is one of the best-preserved ancient Greek temples in existence today, with a stunning location overlooking the Aegean Sea.
Image source: Temple of Poseidon, Sounion

Construction of the Propylaea in Athens begins
437 BC - 432 BC
% complete
Construction of the Temple of Athena Nike in Athens
427 BC - 424 BC
% complete
The Temple of Athena Nike was built on the Acropolis of Athens between 427 BC and 424 BC. It was dedicated to the Greek goddess Athena Nike and was designed by the architect Kallikrates. The temple stood on a high platform and featured four Ionic columns on the front and back. It is known for its frieze depicting scenes from battles and mythological stories. The temple was destroyed during the Turkish occupation of Athens, but it was later reconstructed in the 19th century.
Image source: Temple of Athena Nike

Construction of the Erechtheion in Athens
421 BC - 406 BC
% complete
Construction of the Erechtheion in Athens was a building project that took place from 421 BC to 406 BC. The Erechtheion is a temple located on the Acropolis of Athens and is dedicated to the Greek gods Athena and Poseidon. It was designed by the architect Mnesicles and is known for its unique architectural features, including the Caryatids, which are sculpted female figures used as columns. The construction of the Erechtheion was a significant event in the Greek Golden Age, showcasing the wealth and power of Athens during this period.
Image source: Erechtheion

Philosophy and Science
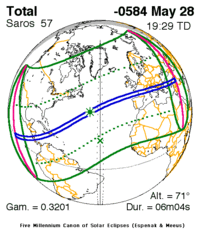
Thales of Miletus predicts a solar eclipse
585 BC
% complete
Thales of Miletus, a Greek philosopher, predicts a solar eclipse which occurred in 585 BC. This prediction is considered to be one of the earliest recorded successful predictions of a celestial event.
Image source: Eclipse of Thales
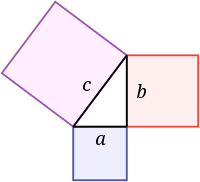
Pythagoras establishes the Pythagorean theorem
530 BC
% complete
Democritus proposes the concept of atoms
460 BC
% complete
Democritus proposes the concept of atoms (460 BC)
Anaxagoras proposes that the moon reflects the sun's light
450 BC
% complete
Zeno of Elea formulates paradoxes
450 BC
% complete
Zeno of Elea formulates paradoxes (450 BC)
Hippocrates establishes the Hippocratic Oath
400 BC
% complete
Hippocrates establishes the Hippocratic Oath in 400 BC. The Hippocratic Oath is a set of ethical guidelines for physicians, emphasizing the importance of treating patients with integrity, confidentiality, and compassion.
Image source: Hippocratic Oath

Socrates' trial and execution
399 BC
% complete
Socrates' trial and execution take place in Athens. He is accused of corrupting the minds of young Athenians and not recognizing the gods recognized by the state. Socrates is found guilty and sentenced to death by drinking a cup of poison hemlock. He accepts the sentence and faces his execution without fear.
Plato founds the Academy in Athens
387 BC
% complete
Plato's "Republic" written
380 BC
% complete
Military and Wars
Battle of Marathon
490 BC
% complete
The Battle of Marathon was a crucial battle between the Greek city-state of Athens and the Persian Empire. It took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. The Persian forces, led by King Darius I, planned to conquer Athens and subjugate the Greek city-states. The Athenians, under the leadership of General Miltiades, assembled a small but determined force to defend their city. Despite being heavily outnumbered, the Greeks managed to defeat the Persians and secure a decisive victory. The Battle of Marathon is considered a turning point in the Greco-Persian Wars and marked the first major Greek victory against the Persians. It also showcased the effectiveness of the hoplite infantry and demonstrated the importance of strategy and discipline in warfare. The Athenians credited their victory to the gods and believed that their faith in the gods had played a significant role in their success.
Image source: Battle of Marathon

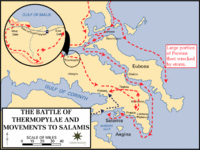
Battle of Thermopylae
480 BC
% complete
The Battle of Thermopylae was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, led by King Leonidas I of Sparta, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. The battle took place in 480 BC and lasted for three days. Despite being heavily outnumbered, the Greeks put up a fierce resistance and inflicted heavy casualties on the Persian forces. However, they were eventually defeated when a local resident showed the Persians a mountain path that allowed them to surround the Greek army. The Battle of Thermopylae is considered a significant moment in Greek history as it showcased the bravery and military prowess of the Greek warriors.
Image source: Battle of Thermopylae

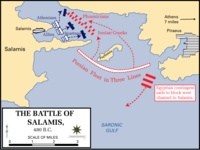
Battle of Salamis
480 BC
% complete
The Battle of Salamis was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states and the Persian Empire in September 480 BC. The Greek victory at Salamis marked a turning point in the Persian Wars and is considered one of the greatest military achievements in ancient Greek history. The Greek fleet, led by Themistocles, lured the Persian fleet into the narrow straits of Salamis, where the larger Persian ships were at a disadvantage. The Greek ships, using their superior maneuverability, were able to outflank and destroy many of the Persian ships, leading to a decisive Greek victory. The Battle of Salamis prevented the Persian Empire from conquering Greece and preserved the independence and cultural heritage of the Greek city-states.
Image source: Battle of Salamis
Battle of Artemisium
480 BC
% complete
The Battle of Artemisium was a naval engagement between the Greek city-states and the Persian Empire during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in August or September 480 BC, parallel to the Battle of Thermopylae on land.
Image source: Battle of Artemisium
Battle of Himera
480 BC
% complete
The Battle of Himera was fought in 480 BC between the Greek city-state of Syracuse and the Carthaginians. The Greek city of Himera had requested help from Syracuse to defend against the Carthaginian invasion. The Syracuse army, led by Gelon, successfully defeated the Carthaginians and secured Himera's independence.
Battle of Plataea
479 BC
% complete
The Battle of Plataea was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, led by the Spartans, and the Persian Empire, led by King Xerxes. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, Greece. The Greek victory in this battle marked the end of the Persian Wars and the beginning of the Golden Age of Athens.
Image source: Battle of Plataea

Battle of Mycale
479 BC
% complete
The Battle of Mycale occurred in 479 BC during the Greco-Persian Wars. It was a naval battle between the Greek city-states and the Persian Empire. The Greek fleet, led by the Athenians, was victorious and managed to liberate the Ionian Greek cities from Persian control. This battle marked the end of Persian expansion into Greece and further established the dominance of the Greek city-states in the Aegean region.
Image source: Battle of Mycale

Peloponnesian War begins
431 BC - 404 BC
% complete
The Peloponnesian War begins in 431 BC and ends in 404 BC. It was a war fought between the two leading city-states of ancient Greece, Athens and Sparta, along with their respective allies. The war was mainly fought on land and sea, with Athens having a strong navy and Sparta having a strong army. The war lasted for 27 years and had a major impact on the balance of power in Greece.
Art and Literature
Aeschylus' play "Persians" premieres
472 BC
% complete
Aeschylus' play 'Persians' premieres in Athens. It is based on the Greek victory over the Persians in the Battle of Salamis. The play is the oldest surviving Greek tragedy and is a patriotic celebration of the Greek triumph.
Aeschylus' play "The Oresteia" premieres
458 BC
% complete
Aeschylus' play 'The Oresteia' premieres in 458 BC. This three-part tragedy tells the story of the House of Atreus and explores themes of justice, revenge, and the transformation of society. It is considered a masterpiece of Greek drama and a reflection of the ideals and values of the Greek Golden Age.
Image source: Oresteia

Sophocles' play "Ajax" premieres
450 BC
% complete
Sophocles' play "Antigone" premieres
441 BC
% complete
Herodotus completes "The Histories"
440 BC
% complete
Herodotus completes "The Histories" in 440 BC. "The Histories" is a historical work written by Herodotus, often referred to as the "Father of History". It is considered to be the first major work of history in Western literature. The book chronicles the Persian Wars and provides valuable insights into the ancient world, including the history, customs, and beliefs of various civilizations.
Image source: Herodotus

Herodotus' "The Histories" published
440 BC
% complete
Herodotus' "The Histories" is a book written in Ancient Greece during the Greek Golden Age. It was published in 440 BC. The book is a collection of historical accounts and observations, covering a wide range of topics including politics, wars, cultures, and traditions of different civilizations. Herodotus is often referred to as the "Father of History" as he was one of the first historians to collect and analyze factual information in a systematic manner.
Euripides' play "Medea" premieres
431 BC
% complete
Sophocles' play "Oedipus Rex" premieres
429 BC
% complete
Sophocles' play 'Oedipus Rex' premieres in Athens. It is believed to have been performed for the first time during the City Dionysia festival in 429 BC. The play tells the tragic story of Oedipus, a king who unknowingly kills his father and marries his mother, fulfilling a prophecy. 'Oedipus Rex' is considered one of the greatest tragedies of ancient Greek theater.
Image source: Oedipus Rex

Euripides' play "Hippolytus" premieres
428 BC
% complete
Euripides' play 'Hippolytus' premieres.
Aristophanes' play "The Clouds" premieres
423 BC
% complete
Aristophanes' play 'The Clouds' premieres in Athens, Greece. The play is a comedy that satirizes philosophers, particularly Socrates, and their teachings. It is known for its portrayal of Socrates as a sophist and its criticism of intellectual pursuits. The premiere of 'The Clouds' is a significant event in the Greek Golden Age as it reflects the growing skepticism towards traditional beliefs and the rise of new ideas and philosophies.
Aristophanes' play "The Birds" premieres
414 BC
% complete
Aristophanes' play 'The Birds' premieres in 414 BC. It is a comedic satire about two men who persuade birds to build a new city in the sky, thereby creating a utopian world. The play critiques the Athenian society and its political system.
Euripides' play "Electra" premieres
413 BC
% complete
Thucydides' "History of the Peloponnesian War" published
411 BC
% complete
Thucydides' 'History of the Peloponnesian War' is published. It is a meticulous and influential account of the conflict between Athens and Sparta, covering events from 431 BC to 411 BC.
Aristophanes' play "Lysistrata" premieres
411 BC
% complete
Aristophanes' play 'Lysistrata' premieres in Athens. It is a comedic play about a woman named Lysistrata who convinces the women of Greece to withhold sexual privileges from their husbands as a way to force them to negotiate peace and end the Peloponnesian War.
Euripides' play "The Bacchae" premieres
405 BC
% complete
Euripides' play "The Bacchae" premieres in Athens, Greece. The exact date is believed to be around 405 BC, towards the end of Euripides' life. The play is based on the mythical story of Dionysus, the god of wine, and his revenge on Thebes for denying his divinity. It explores themes of religion, power, and the clash between the rational and irrational. The play was not well-received during Euripides' lifetime but has since been recognized as one of his greatest works and an influential play in Greek tragedy.
Image source: The Bacchae

Thucydides' "The Funeral Oration of Pericles" written
404 BC
% complete
Thucydides' 'The Funeral Oration of Pericles' is a famous speech given by Pericles, a prominent statesman and general of Athens, during the Peloponnesian War. The speech was delivered in 404 BC, at the end of the first year of the war. Pericles delivered the speech to honor the soldiers who had died in battle and to inspire the living to continue fighting for their city-state. The speech is known for its emphasis on Athenian democracy and the values of the city-state.
Politics and Democracy
Pericles' Funeral Oration
431 BC
% complete
Pericles' Funeral Oration was a speech given by the Athenian statesman Pericles during the Peloponnesian War. It was delivered in 431 BC to honor the Athenian soldiers who had died in battle. In the speech, Pericles praised the Athenian democracy and its values, highlighting the virtues of the fallen soldiers and emphasizing the importance of defending Athens and its way of life. The Funeral Oration is considered one of the greatest examples of ancient Greek rhetoric and a celebration of Athenian democracy and culture.
Image source: Pericles's Funeral Oration

Key Facts
- The Greek Golden Age is also known as the Age of Pericles, named after the influential Athenian statesman.
- It was a time of great artistic achievements in architecture, sculpture, and drama, with famous works like the Parthenon and the tragedies of Sophocles and Euripides.
- During this period, the concept of democracy was developed in Athens, making it one of the first democratic cities in the world.
- The Greek Golden Age saw the rise of famous philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, who greatly influenced Western philosophy.
- The Olympic Games, which began in ancient Greece, were revived during this period as a major sporting event.
Source
This Greek Golden Age timeline was generated with the help of AI using information found on the internet.
We strive to make these timelines as accurate as possible, but occasionally inaccurates slip in. If you notice anything amiss, let us know at [email protected] and we'll correct it for future visitors.
Create a timeline like this one for free
Preceden lets you create stunning timelines using AI or manually.
Customize your timeline with one of our low-cost paid plans
Export your timeline, add your own events, edit or remove AI-generated events, and much more
Free
$
0
free forever
No credit card required.
Basic
$
10
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Pro
$
16
/month
billed annually
Cancel anytime.
Common Questions
Can I cancel anytime?
Yes. You can cancel your subscription from your account page at anytime which will ensure you are not charged again. If you cancel you can still access your subscription for the full time period you paid for.
Will you send an annual renewal reminder?
Yes, we will email you a reminder prior to the annual renewal and will also email you a receipt.
Do you offer refunds?
Yes. You can email us within 15 days of any payment and we will issue you a full refund.
What if I have more questions?
Check out our pricing docs or send us an email anytime: [email protected].